Table of Contents
A Strategic HR Organization encompasses plans and actions of a comprehensive network of HR professionals, leaders, and stakeholders dedicated to the design, execution, and enhancement of strategic human resource management efforts within a business. This construct goes well beyond conventional (transactional) HR, emphasizing alignment between HR strategies and the overarching business goals. By fostering a collaborative and systemic approach, a Strategic HR Organization aims to leverage human capital efficiently, ensuring the company's workforce is well-equipped, engaged, and aligned with the enterprise's mission and vision.
Such a strategic approach underscores the importance of dynamic organizational alignment, adaptation, and advancement through continuous evaluation and improvement to ensure sustainability. It also focuses on proactively activating and accelerating its talent to maximize impact, making HR not just a supporting function but a growth enabler in steering the company's future direction, thereby showcasing HR’s evolving role.
The criticality of using a balanced approach to creating a strategic HR organization
In a challenging business and labor environment that makes it difficult to keep up with the accelerated pace of change, running an effective, efficient, and desired organization may seem difficult. When adding a desire for companies to maintain and transcend that state, then almost feels utopian. In essence, what organizations aspire to is to be “sustainable”. By definition, a sustainable organization is able to maintain healthy financials, satisfied customers, effective processes, and an engaged workforce that keeps learning and growing on an ongoing basis.
The key is to maintain a balance across the critical dimensions at play. We have already seen successful and enduring examples of this in strategic approaches such as the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) and later the HR Scorecard, introduced years ago, which translates an organization's vision and strategy into a coherent set of performance measures, critical dimensions of a business's health, and corresponding metrics in the management of a company. Other approaches have also emerged, including OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) and Agile performance management. The principles and focus on holistic, adaptable, and balanced dimensions originated with the BSC methodology have influenced many of these newer approaches. The reason is that creating sustainability through balance is a universal law of nature.
In following these principles, establishing a sustainable strategic HR organization requires integrating, harmonizing, and balancing diverse fundamental dimensions to sustain a virtuous cycle of learning and growth for the workforce and the organization.
The dimensions of an integrated talent and organizational sustainment framework
At Wowledge, we have created a comprehensive blueprint we call the “Integrated Talent and Organizational Sustainment Framework,” which represents a holistic approach to the areas a strategic HR organization should drive to maximize its impact on the business and workforce in the rapidly evolving environment we face today.
This framework ensures that every HR initiative propels the company closer to its goals. Navigating the complex interplay between dynamic external changes and internal demands requires a systemic HR approach that balances these dimensions harmoniously. These dimensions—ranging from organizational alignment to continuous improvement—not only pave the way to providing the business with a competitive advantage rooted in its human capital but also fortify the organization's adaptability and long-term sustainability.
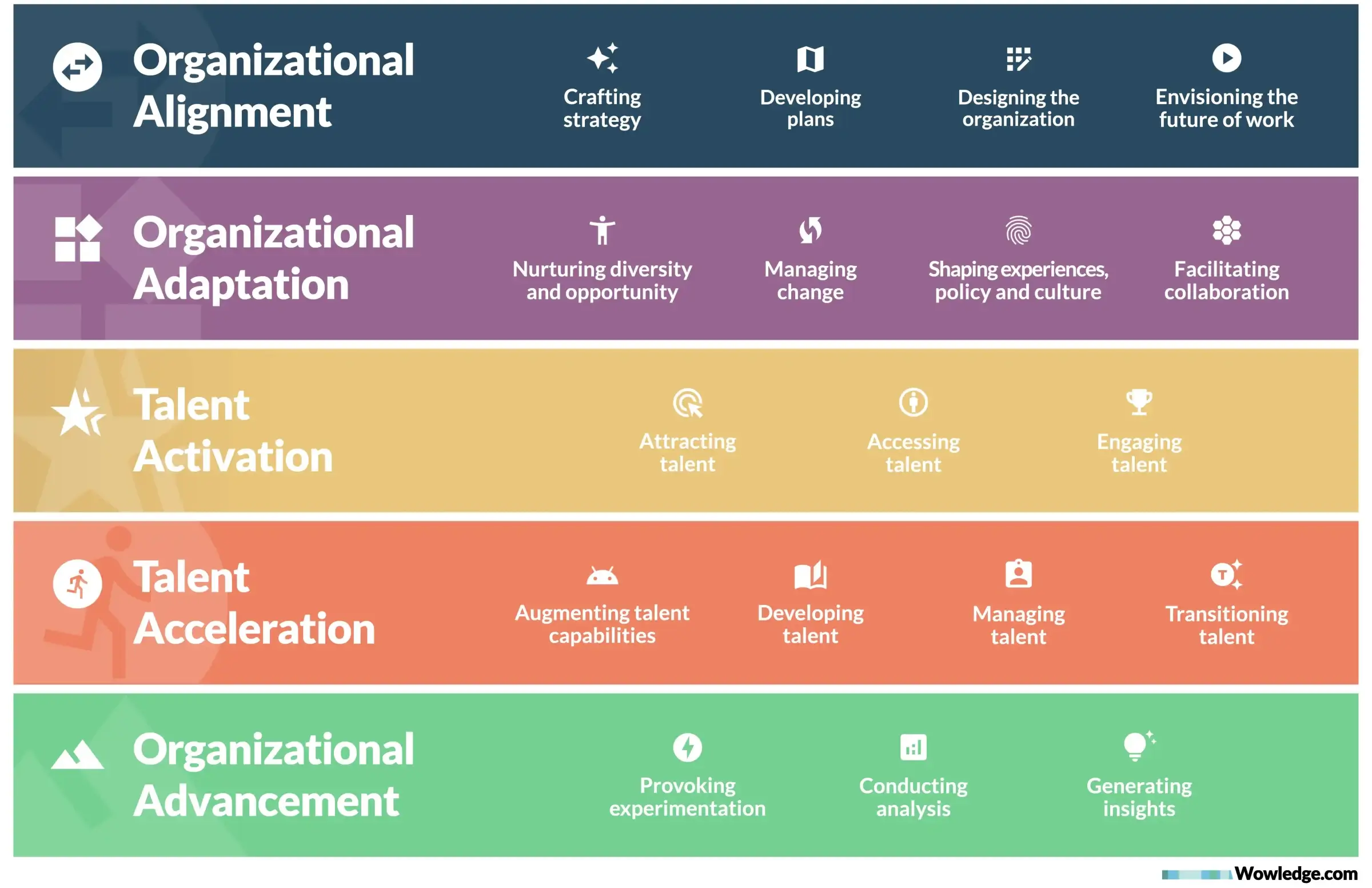
1. Organizational Alignment
An essential function of strategic HR organizations is to ensure that company strategies, resources, and employees' efforts are in sync. When HR ensures its initiatives are prioritized and that every policy, process, and program is directly tied to the broader business objectives, the company can foster unity and efficiency in pursuing its near-term and future strategic ambitions. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension include crafting strategy, developing plans, designing the organization, and envisioning the future of work.
2. Organizational Adaptation
In an era of unprecedented change, the capacity for a strategic HR organization to enable company-wide adaptation is crucial. By building resilience, flexibility, and an inclusive culture, HR helps the company respond swiftly to internal and external shifts, such as market disruptions, technological advancements, or changes in workforce dynamics. This agility is fundamental for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving long-term sustainability. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension include nurturing diversity and opportunity, managing change, shaping experiences, policy, and culture, and facilitating collaboration.
3. Talent Activation
The workforce is rapidly transforming, not only in terms of the types of skills and capabilities available in the market, but also in how people choose to work, whether as employees, contingent workers, freelancers, or part of the gig economy. Organizations need to design programs that leverage these dynamics to maintain effective, efficient business operations. By engaging and leveraging the full spectrum of workers, strategic HR organizations tap into a vast, versatile talent pool, driving innovation and providing the agility to scale resources in line with market demands. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension include attracting, accessing, and engaging talent.
4. Talent Acceleration
Due to the rapid adoption of emerging technologies and the evolution of market demands and skill requirements, organizations need to prioritize the rapid development of employee competencies and career pathways. Strategic HR organizations ensure the company has a robust, skilled, and prepared workforce, ready to take on emerging opportunities and challenges, thereby securing the company's future and competitive position. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension include augmenting talent capabilities and developing, managing, and transitioning talent.
5. Organizational Advancement
For a strategic HR organization, the ability to continuously learn and advance is vital in fostering a culture of perpetual growth and evolution. By championing experimentation and continuous improvement, HR ensures that the function doesn't just react to changing business needs but actively shapes forward-looking programs that help the business and individuals thrive. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension include provoking experimentation, conducting analysis, and generating insights.
When organizations fail to leverage all five dimensions, they face challenges in harmonizing their goals, effectively adapting to changing conditions, maximizing the impact of their human capital, and ultimately sustaining their operations in the long run. It generates shortcomings that often lead to inefficiencies, decreased engagement, lowered retention of top talent, and a lack of competitiveness, hindering the company’s ability to thrive in an ever-evolving business environment.
The evolving role of HR
As businesses grapple with rapid technological change, geopolitical shifts, and a dynamic global talent market, the need for a proactive, agile HR function has never been more pressing. An HR organization that has incorporated a balanced, sustainable approach to its strategic efforts aligns with these evolutions, playing a critical role in translating business objectives into human capital strategies. As they build strong relationships with business leaders, develop an understanding of industry trends, and leverage technology, strategic HR organizations ensure that the business and workforce are not only prepared for the future but thrive in it.

FAQs
What early signals indicate the organization is unbalanced across strategic HR dimensions?
Persistent rework, initiative churn, or conflicting priorities suggest weaknesses in Organizational Alignment. Slow adoption, shadow processes, or “policy exceptions” point to Adaptation gaps, while stalled internal mobility and skill bottlenecks expose shortfalls in Activation and Acceleration. If formal lessons-learned analyses are not acted upon and do not change outcomes, Advancement is underpowered.
How should HR sequence work when the budget is limited?
Stabilize Alignment first so goals, governance, and decision rights are explicit, then fund one or two Adaptation enablers that remove friction to change. Prioritize Activation items that improve hiring quality and time-to-productivity in pivotal roles, and layer in Acceleration for those same roles to compound benefits. Reserve Advancement spend for measurement and feedback loops that protect ROI.
What governance model keeps the framework from becoming confined to HR?
Create a small cross-functional steering group with business leaders and finance that reviews and approves priorities and assesses outcomes on a fixed cadence. Use a standard service or initiative request intake process and scoring method across all dimensions to drive investment (time, effort, budget) decisions that are objectively based. Tie executive goals to adoption and impact metrics so governance concentrates on results, not activity volume.
How can HR integrate OKRs or a Balanced Scorecard with the sustainment framework?
Anchor company and function-level OKRs to the outcomes of each dimension, so work is tied directly to business goals. Use the Balanced Scorecard perspectives to pressure-test completeness and ensure people, process, customer, and financial effects are represented. Refresh targets quarterly, but stabilize definitions and data sources to maintain comparability.
About Wowledge
Wowledge is the implementation-first platform designed for lean HR teams and consultants who need to design and scale strategic HR programs efficiently—without starting from scratch.
Our members gain access to continuously updated best practices, step-by-step guidance, expert-built tools, and customizable templates—all structured to accelerate the development and implementation of key HR programs.
Recognizing that every organization operates at different levels of sophistication, Wowledge’s scalable system of best practices follows a stage-based approach—Core, Advanced, and Emerging—ensuring HR professionals can implement solutions tailored to their organization’s unique needs and goals.
Your Shortcut to Amplifying HR Impact!
Get started for FREE! Learn more.