The Integrated Talent and Organizational Sustainment Framework is a holistic and balanced approach, designed to elevate HR organizations into strategic partners within their businesses. By holistically addressing five key dimensions —Organizational Alignment, Organizational Adaptation, Talent Activation, Talent Acceleration, and Organizational Advancement— this framework empowers HR teams to align their human capital with overarching business goals, drive organizational resilience, and champion continuous improvement. Uniquely poised for the modern enterprise, this framework enables HR’s evolving role as a critical driver of sustainable growth and competitive advantage. The framework is ideal for organizations aiming to seamlessly integrate talent optimization with their strategic roadmap regardless of the company’s size, stage, or sophistication level.
Why use it
As the evolving role of HR within contemporary business environments necessitates a shift from transactional to strategic human resource management, the "Integrated Talent and Organizational Sustainment Framework" provides direction for this transition. It enables HR organizations to contribute to the broader strategic objectives of the company proactively. By adopting a balanced approach, this framework ensures that HR practices are not just about covering pressing efforts on talent acquisition or workforce management but also about ensuring that strategic HR initiatives are synchronized with business imperatives. With an emphasis on holistic development and sustainment, the framework aids HR leaders in navigating the challenges of the modern business landscape to stay current and increase their value as strategic business partners.
The framework highlights the critical role that strategic HR organizations play in aligning company strategies, resources, and employee efforts with overarching business objectives, promoting unity and efficiency (Organizational Alignment). It acknowledges that in today's rapidly changing environment, HR's ability to foster resilience, flexibility, and inclusivity enables companies to swiftly respond to shifts like market disruptions, technological advances, and workforce dynamics, ensuring a competitive edge and long-term sustainability (Organizational Adaptation). Furthermore, the model recognizes the evolving nature of the workforce and how modern organizations should engage a diverse talent pool, from traditional employees to freelancers, optimizing business operations (Talent Activation). It also emphasizes rapid skill development in response to technological and market changes, ensuring a prepared and skilled workforce ready for future challenges (Talent Acceleration). Finally, through continuous learning and a commitment to innovation, HR can shape forward-looking programs, nurturing a culture of growth and continuous evolution (Organizational Advancement).
Overlooking any of the five dimensions can lead organizations to face hurdles in goal alignment, adaptability to change, or harnessing the full potential of their talent. Such oversights often translate into operational gaps, diminishing engagement, a revolving door for top talent, and losing competitive relevance. In a constantly shifting business world, all five dimensions have become fundamental to building a lasting strategic HR organization that ensures both the workforce and the business benefit from a continuous cycle of learning and growth.
Wowledge’s Integrated Talent and Organizational Sustainment Framework
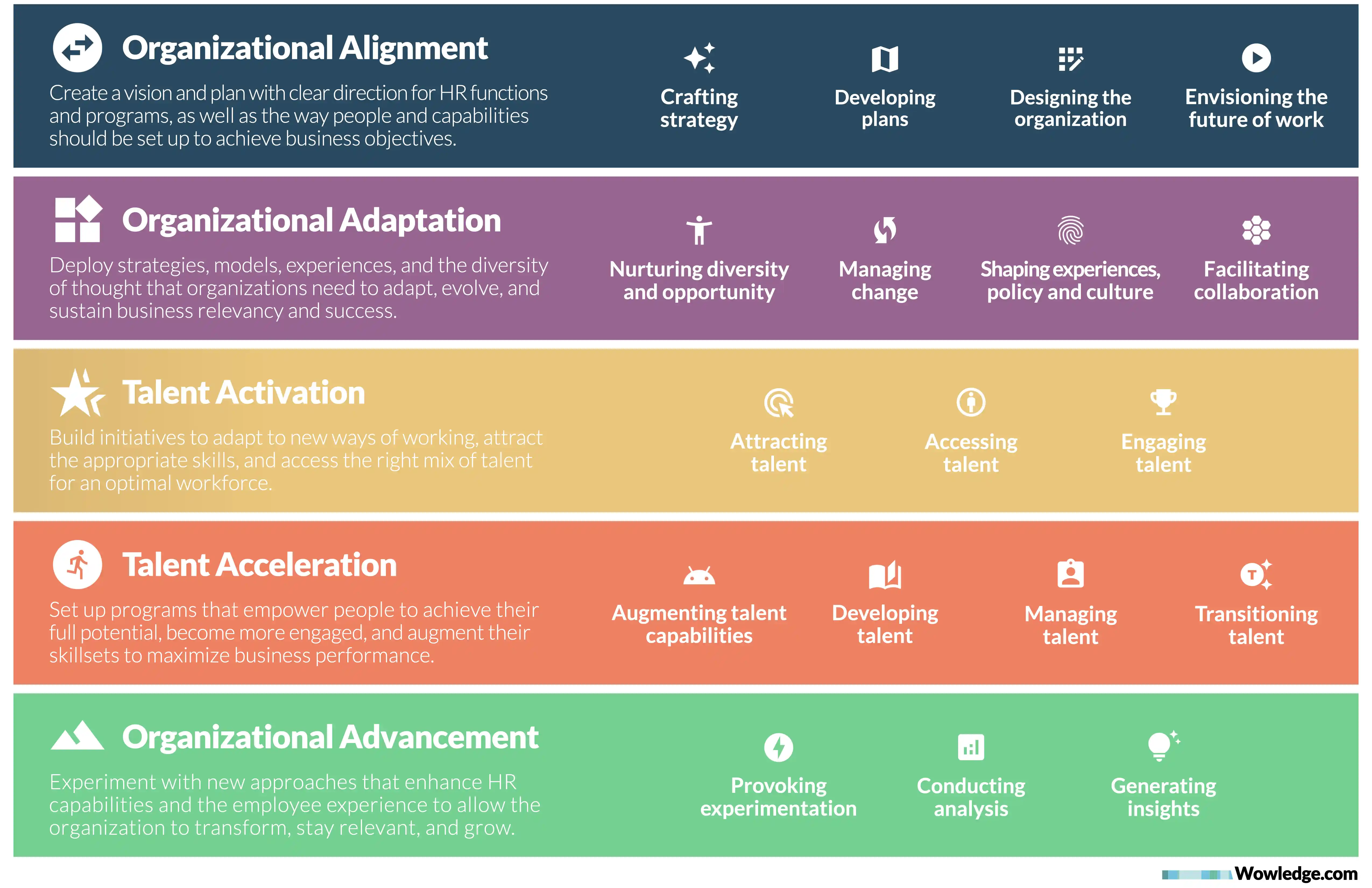
Organizational Alignment
Focuses on all the activities needed to create a vision and plan with clear direction for HR functions and programs, as well as the way people and capabilities should be organized to achieve business objectives. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension are:
- Crafting strategy – develop comprehensive approaches to manage human capital aligning with organizational goals. It necessitates identifying the current and future needs of the organization and formulating strategies to address them.
- Developing plans – create detailed and structured roadmaps to implement HR strategies and initiatives effectively. This involves setting clear objectives, timelines, and actionable steps to achieve goals.
- Designing the organization – structure the workforce and define roles and responsibilities to optimize productivity and operational efficiency. It involves creating organizing principles that support the company’s strategic objectives, foster collaboration, and promote a positive work environment.
- Envisioning the future of work – anticipate and prepare for emerging trends, technologies, and challenges that will shape the workplace. It requires a forward-thinking approach to adapt to changes in the work environment, workforce expectations, and employment models.
Organizational Adaptation
Addresses practices to deploy strategies, models, experiences, and the diversity of thought organizations need to adapt, evolve, and sustain business relevancy and success. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension are:
- Nurturing diversity and opportunity – design and implement policies and practices to ensure a diverse, equitable, and inclusive work environment. It demands creating mechanisms to identify appropriately aligned opportunities to leverage varied backgrounds, perspectives, and abilities in response to business and operational needs.
- Managing change – deploy approaches to ensure transitions are smooth and the workforce is adaptable and resilient in the face of change. This might include changes in organizational structure, processes, or strategy, helping to maintain morale, productivity, and alignment with organizational objectives during periods of transformation.
- Shaping experiences, policy, and culture – develop a culture and employee experience that promotes alignment with organizational values, enhances engagement, and supports well-being. It requires creating policies and procedures that are not only compliant with laws and regulations but also foster a healthy and productive work environment.
- Facilitating collaboration – implement tools, technologies, and strategies to enhance and reward knowledge sharing, collective problem-solving, and cooperation among employees, teams, and functions. This involves developing communication channels, team-building activities, and collaborative platforms that help in breaking silos and fostering a sense of community and shared purpose.
Talent Activation
Centers around the need to build initiatives to adapt to new ways of working, attract the appropriate skills, and access the right mix of talent for an optimal workforce. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension are:
- Attracting talent – focus on bringing skilled and suitable candidates to the organization. It involves creating a compelling employer brand and employee value proposition (EVP) to appeal to potential employees. This is furthered by fostering an inclusive and vibrant organizational culture and offering competitive benefits and growth opportunities to ensure the organization stands out as an employer of choice.
- Accessing talent – evaluate and determine the suitability of talent for permanent or temporary roles within the organization whether as employees or contingent workers. It implies meticulously analyzing various aspects of prospective workers to ensure they possess the required competencies and align with the organization's values and goals.
- Engaging talent – implement strategies to ensure workers are motivated, committed, and fully involved. It encompasses activities aimed at fostering a positive work environment, recognizing and rewarding contributions, and providing opportunities for professional development and growth.
Talent Acceleration
Emphasizes setting up programs to empower people to achieve their full potential, become more engaged, and augment their skill sets to maximize business performance. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension are:
- Augmenting talent capabilities – strategically enhancing the skills, abilities, and knowledge of the workforce to meet current and future organizational needs. It includes providing resources that allow employees to enhance their capabilities. This involves leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) to accelerate and adapt work in a rapidly changing business landscape.
- Developing talent – undertake a structured process to nurture employees' professional growth and career progression. Through a combination of formal learning, on-the-job experiences, and relationship-building opportunities, it ensures that employees are equipped with the competencies needed to excel in their roles on an ongoing basis.
- Managing talent – establish a suite of activities focused on optimizing the performance and potential of the organization’s workforce. It represents the processes needed to align individual goals with organizational objectives, identify high-potential employees, and ensure a consistent approach to managing talent across the organization.
- Transitioning talent – facilitate the movement of employees within, into, or out of the organization. This could involve internal promotions, role changes, onboarding new hires, or managing exits and retirements. It requires developing strategies and processes to ensure smooth transitions, including clear communication, adequate support, and knowledge transfer.
Organizational Advancement
Promotes experimenting with new approaches that enhance HR capabilities and the employee experience to allow the organization to transform, stay relevant, and grow. The specific practice categories that enable this dimension are:
- Provoking experimentation – create an environment conducive to innovation that encourages HR professionals, their stakeholder ecosystem, and employees in general to try out new ideas, methods, or approaches that might provide an optimal alignment with the organization’s context and therefore, create better results over time.
- Conducting analysis – systematically examine data or information by integrating diverse datasets and breaking them into their component parts to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. It enables HR to optimize their strategies and interventions, addressing issues such as employee turnover, performance, engagement, or productivity.
- Generating insights – interpret data and information to understand trends and insights that can inform strategic decisions and actions. HR leverages data from people analytics and employee feedback to gain a deeper understanding of the workforce and create value by improving decision-making, enhancing the employee experience, and better aligning talent strategies with organizational goals.

