Table of Contents
As the digital revolution continues to grow and transform work and how it is accomplished, organizations are moving quickly to figure out its potential to reshape workforce experiences and boost productivity. Integrating advanced platforms with embedded artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities is at the heart of this transformation. Although this progression sounds technical, HR practitioners and strategists should recognize the new challenge of creating an AI-native workforce ecosystem that seamlessly blends human judgment with technological prowess, fostering continuous learning, innovation, and inclusivity along the way.
Just a few years ago, a new wave of artificial intelligence (AI) and related technologies began changing the landscape of workplaces around the globe. Many organizations championed the implementation and experimentation of this new technology. Making AI a business value accelerator meant multiplying the impact of its products and services on customers as AI's promises became feasible, more affordable, and within reach. However, this requires building an AI-native workforce ready to exploit such technologies' capabilities and advantages.
For example, one of the world's leading and most prominent technology companies, Amazon, has proven that AI capabilities make a real difference for its customers. Some examples include reducing onboarding time with Amazon Q Business, cutting document review time in half using Amazon Textract, and improving operational efficiency with predictive maintenance using Amazon Monitron. It is not a surprise that the focus of digital transformations mainly remains on productivity and operational efficiency.
The nature of the digital revolution is no longer limited to a person, a group of people, an organization, a public or private domain, or a geographical region. Employees have started experimenting at home in their personal “playgrounds” using open-access AI tools to assist them in simple, non-complex work-related tasks. The question becomes how organizations can leverage and empower an AI-native workforce more strategically, responsibly, and driven by clear outcomes.
Some organizations struggle to fully leverage digital technologies, hindered by legacy systems, cultural inertia, employee resistance, and a lack of strategic alignment. At the same time, the workforce's readiness to embrace, adopt, and boost productivity using AI tools has become a requirement for building an organization’s leadership position. The workers are at the core of the issue for HR and business leaders as the key enablers and agents of transformation efforts.
So, what do opportunities, challenges, and pathways to building a future-ready, digitally enabled, and AI-native workforce look like today? Will workers become engaged and empowered to lead an organizational technology-driven makeover? What successful implementations and critical barriers to digital transformations exist, and how can organizations start breaking them down?
The AI-native imperative for a digital-first world
The digital revolution has irrevocably changed the work landscape, much like the Industrial Revolution did almost two centuries earlier. Employees are “gifted” the power to nudge their performance levels with a simple click on the AI icon embedded in various work platforms, tools, and devices.
“AI Native” refers to a future state where all system components use AI in and among each other. It represents an ecosystem (e.g., work processes and all their enabling technologies) where AI technologies support its various elements. It means a state that leverages AI in every aspect of a process lifecycle, including controlling how those are implemented, monitored, and managed with AI.
On an organizational level, a digital-first, AI-native workforce strategy builds human capabilities that enable such a transformation. It reimagines and transforms how employees interact with technology, workflows, and each other. It prioritizes:
Enhancing the employee experience (EX)
- Improved communication and collaboration: Digital platforms facilitate seamless communication and collaboration across teams, departments, and geographical boundaries. Tools like instant messaging, video conferencing, and project management software enhance communication efficiency and foster a more connected and engaged workforce. Platforms enable seamless human-machine collaboration, leveraging AI to automate repetitive tasks and support strategic decision-making.
- Increased flexibility and autonomy: Digital technologies empower employees with greater flexibility and independence in their work arrangements. Remote work options, flexible schedules, and mobile access to work tools give employees greater control over their work-life balance.
- Personalized learning and development: Digital platforms offer personalized learning experiences, enabling employees to access training resources, develop new skills, and advance their careers at their own pace and with their interests. AI-powered tools provide tailored recommendations, learning paths, and real-time support to enhance employee satisfaction and productivity.
Boosting productivity and efficiency
- Automation of routine tasks: AI-powered tools can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
- Data-driven decision-making: Digital platforms provide access to real-time data and analytics, enabling data-driven decision-making across all levels of the organization.
- Improved operational efficiency: Streamlined workflows and automated processes enhance operational efficiency, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall organizational performance.
Fostering adaptability and innovation
- Agility and responsiveness: Digital technologies enable organizations to be more agile and responsive to changing market conditions and customer demands. Digital tools are designed to accommodate diverse needs, creating a more inclusive and boundaryless workplace that supports all employees.
- Cultivation of a culture of innovation: A digital-first culture encourages experimentation, innovation, and the exploration of new ideas and technologies. By embedding AI into workflows, organizations can foster a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement, empowering workers to address ethical, safety, and privacy concerns firsthand.
- Enhanced competitiveness: By leveraging digital technologies, organizations can gain a competitive edge in the marketplace by improving their speed, agility, and ability to deliver exceptional customer experiences. It encourages internal change champions and supporters who will advocate for best practices in their teams and project groups.
Organizations leading the way
Some high-profile organizations have successfully embraced digital transformation initiatives to enhance workforce experiences and drive business growth. They serve as examples (and guides) to inspire thinking about how advanced technology can be leveraged to improve productivity, performance, and talent outcomes. Here are a few prominent examples:
1. Microsoft has embedded AI into its productivity tools, such as Microsoft Viva, to create a more connected and engaged workforce. Viva Insights uses AI to provide personalized recommendations for well-being, productivity, and collaboration, enabling employees to balance their workloads effectively.
2. Accenture has implemented an AI-first approach through its "SynOps" platform, which optimizes operations by combining AI, analytics, and human expertise. This has transformed how the organization delivers client services and internal processes, fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
3. Siemens has embraced digital transformation through its "Mindsphere" platform, an industrial IoT (“Internet of Things”) ecosystem that leverages AI to drive operational efficiency and workforce productivity. This platform enables employees to interact with real-time data, improving decision-making and adaptability.
4. Unilever leverages AI-driven talent management tools to identify skill gaps, recommend personalized learning programs, and enhance diversity and inclusion initiatives. By integrating AI into its talent strategy, Unilever has built a more agile and inclusive workforce.
5. Spotify has built a highly digital and data-driven workplace culture. The company leverages AI-powered algorithms to personalize user music recommendations, analyze listening trends, and identify emerging artists. Internally, Spotify utilizes digital tools for communication, collaboration, and performance management, fostering a highly agile and innovative work environment.
6. Google emphasizes a data-driven approach to decision-making, utilizing AI and machine learning to optimize its search algorithms, generate code, develop new products, and improve employee productivity. Google also invests heavily in employee training and development, providing access to cutting-edge technologies and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
7. Salesforce has successfully leveraged cloud computing and AI to transform its sales and customer service operations. The company's CRM platform utilizes AI-powered features to predict customer behavior, personalize customer interactions, and improve sales outcomes. Salesforce also prioritizes employee development, offering a wide range of online training courses and certifications to upskill its workforce.

Challenges HR faces in enabling digital workforce experiences
Despite the potential benefits of digital transformation, organizations face significant challenges in implementing and sustaining these initiatives. All of the barriers and difficulties are real and valid and require careful consideration from stakeholders. From the lack of technical skills to the gaps in organizational strategy, leaders have to address and mitigate new risks. HR leaders must be aware of and exercise diligence over these internal barriers and generate responsive strategies to mitigate them to properly prepare an AI-native workforce.
Resistance to change
Many organizations have risk-averse cultures that resist the rapid adoption of new technologies. Employees and leaders often fear that automation and AI will replace jobs, leading to pushback rather than collaboration and creating resistance to adopting new technologies.
Lack of digital literacy
Employees' lack of digital and AI literacy can hinder their adoption and utilization of new technologies. The shift to AI-first workflows requires employees to develop new digital and analytical skills. Organizations often struggle to upskill their workforce at scale, leading to uneven adoption and frustration.
Aversion to new ways of working
Employee resistance to changes in their job requirements and established work habits and routines can create inertia and exacerbate a lack of trust in new ways of working when adopting new digital tools is required.
Insufficient organizational alignment
Digital transformation initiatives often fail due to a lack of strategic alignment between organizational goals and technology investments and when key stakeholders speak from self-preservation and miss the growth imperatives. Without clear priorities and committed leaders, resources are wasted, and impact is diluted.
Equity and accessibility gaps
Implementing digital tools can inadvertently exclude certain groups, such as employees with disabilities or those in remote regions with limited connectivity. Ensuring inclusivity requires deliberate design and investment from all leaders and teams. It also necessitates a mind-shift from fear of failing to opportunities-driven solutions.
Investment in legacy systems and infrastructure
Outdated IT systems and processes can hinder the seamless integration of AI-powered tools. Many organizations are constrained by existing technologies that cannot support or be integrated with and into advanced technologies and modern workflows. Similarly, data privacy and security concerns increase with the adoption of new technology. Data breaches and cyberattacks are a new normal that organizations have been learning to live with. It is not a question of “if” it happens; it is a question of “when.” The increased reliance on and use of digital technologies makes organizations and their people vulnerable and requires updated policies, procedures, and practices.
The AI adoption and employee readiness framework
The ability of an organization to successfully adopt and implement AI technologies is a function of its a) commitment and acquisition of these capabilities, which are then influenced by b) employee readiness to adapt to them. Careful consideration should go into developing strategies that enable and support an AI-native workforce to increase the likelihood of acceptance and adoption, which requires robust assessment, planning, and change management strategies.
A three-by-three framework expands the dimensions of AI adoption and employee readiness to low, moderate, and high levels to help organizations identify specific and likely challenges and opportunities as they navigate the intersection of AI-enabled workflows and workforce preparedness. The matrix below provides a granular perspective and allows for a more nuanced understanding of what will be faced when installing and implementing AI technologies. Focused actions in each offer insights into how HR and leadership teams can plan to intervene and mitigate the risks at each assessed level.
Matrix Dimensions
AI Adoption:
- Low: Limited AI integration or no use of AI tools.
- Moderate: Partial implementation of AI in specific departments or processes, with room for improvement.
- High: Comprehensive adoption and integration of AI across the organization.
Employee Readiness:
- Low: Most employees lack awareness, skills, or willingness to engage with AI tools.
- Moderate: Some employees or groups are equipped and willing to engage with AI, but others require training or mindset shifts.
- High: All employees in key, value-generating functions and most employees in support functions are highly skilled, knowledgeable, and proactive in using AI to improve workflows.
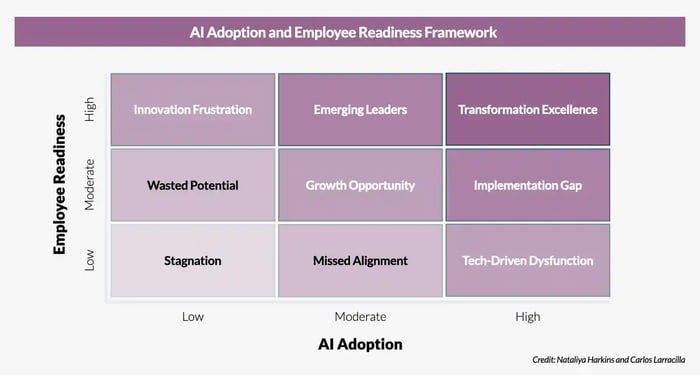
Quadrant Descriptions
Row 1: Low Employee Readiness
Low AI Adoption (Stagnation Zone):
- Description: Neither employees nor the organization are ready for AI transformation.
- Challenges: Lack of innovation, inefficiencies, and risk of falling behind competitors.
- Focused Actions: Build awareness about AI’s potential for leadership and employees.
Moderate AI Adoption (Missed Alignment):
- Description: The organization has adopted AI in a few areas, but employees are not prepared to engage with it.
- Challenges: Limited use of AI tools due to resistance or lack of skills, leading to wasted investments.
- Focused Actions: Provide foundational training programs to align employees with the organization's AI goals.
High AI Adoption (Tech-Driven Dysfunction):
- Description: AI tools are widely implemented, but employee readiness remains very low.
- Challenges: Over-reliance on AI without human expertise can result in inefficiencies, poor implementation, and resistance.
- Focused Actions: Balance technology investments with a robust upskilling program.
Row 2: Moderate Employee Readiness
Low AI Adoption (Wasted Potential):
- Description: Employees are willing and somewhat prepared to adopt AI, but the organization has not prioritized technology investment.
- Challenges: Employee enthusiasm and potential go underutilized.
- Focused Actions: Begin exploring AI tools that align with existing employee skills and processes.
Moderate AI Adoption (Growth Opportunity):
- Description: Both employees and the organization are beginning to embrace AI, but efforts are not yet cohesive or optimized.
- Challenges: Limited scalability of AI initiatives due to partial readiness on both sides.
- Focused Actions: Align strategic AI goals with employee development initiatives to build momentum.
High AI Adoption (Implementation Gap):
- Description: The organization has invested in AI tools, and employees are moderately ready but require further development to optimize usage.
- Challenges: AI adoption outpaces workforce capabilities, leading to a lag in achieving ROI.
- Focused Actions: Conduct targeted upskilling and foster cross-functional collaboration.
Row 3: High Employee Readiness
Low AI Adoption (Innovation Frustration):
- Description: Employees are highly skilled and eager to adopt AI, but the organization has not implemented the necessary technology.
- Challenges: Employees may become disengaged due to a lack of innovation opportunities.
- Focused Actions: Prioritize immediate AI technology investments and provide platforms for employees to experiment and lead AI initiatives.
Moderate AI Adoption (Emerging Leaders):
- Description: The organization has implemented AI in some areas, and employees are ready to take it further.
- Opportunities: Strong potential for innovation and efficiency gains as employees drive the adoption process.
- Focused Actions: Scale successful AI projects and empower employees to lead adoption efforts across departments.
High AI Adoption (Transformational Excellence):
- Description: The organization and employees fully align on AI, leveraging technology and human expertise to drive innovation.
- Opportunities: Sustained competitive advantage, optimized processes, and a culture of continuous improvement.
- Focused Actions: Maintain a balance of ongoing training and investment to stay ahead in emerging AI trends.
Overcoming challenges on the path to an AI-native workforce
As an HR practitioner, it is essential to strategically and holistically address the challenges faced in today's workplace. Enabling a digital-first, AI-native workforce experience is not just a technology readiness challenge but a cultural and strategic one as well. Organizations must prioritize agility, inclusivity, and innovation to navigate the complexities of digital transformation successfully. Organizations can build future-ready ecosystems that empower employees and drive sustained success in the AI era by learning from industry leaders and tackling common challenges with targeted strategies.
Based on an organization's current level of readiness, the desired or planned extent of AI integration, and the pace of transformation, the following recommendations will help establish a sustainable path for enhancing workforce experiences with new technologies. Organizations must ensure their employees receive proper training, preparation, and trust in leveraging AI, creating a future-proof workforce that can capitalize on emerging opportunities.
1. Cultivate a digital-first culture
- Promote a mindset of experimentation and learning by encouraging AI testing, celebrating successes, and normalizing failure as part of innovation.
- Engage leaders at all levels to champion digital transformation and address fears around job displacement through transparent communication.
2. Invest in workforce upskilling and reskilling
- Develop comprehensive learning programs focusing on digital literacy, AI fluency, and critical thinking.
- Partner with educational institutions and technology providers to create accessible training opportunities.
3. Modernize the technology infrastructure
- Transition from legacy systems to cloud-based platforms that support scalability and AI integration.
- Ensure data interoperability to enable seamless workflows and analytics.
4. Align technology with organizational goals
- Conduct a thorough needs assessment to identify priority areas for AI deployment.
- Establish cross-functional teams to ensure technology investments align with business objectives and employee needs.
5. Design for inclusion and accessibility
- Incorporate universal design principles into digital tools to accommodate diverse employee needs.
- Provide robust support systems, such as AI-powered virtual assistants, to enhance employee accessibility.
Relevant Practices & Tools
Core HR Practices to Activate the Digital Transformation Journey. >
Digital transformation integrates digital tools, technology, and culture into all aspects of a business, fundamentally altering how an organization operates and delivers value to customers... more »
Driving Adoption of the Digital Future to Optimize the Return on Digital Investments. >
The digital transformation will deliver a new way of operating for the business. It establishes a new status quo for what employees expect, how they work individually or in teams... more »
Accelerating the Organization Toward the Future by Building a Digital Culture. >
Companies successfully transforming their operations to a digital environment accumulate organizational momentum toward the new digital future... more »
Employing Advanced Stakeholder Engagement Techniques to Reinforce the Criticality of the Targeted Change. >
When done effectively, stakeholder engagement creates trust with the initiative team, generates honest dialogue to build support for the changes, and reduces the potential for conflict... more »
The Stakeholder Engagement Plan Template: Identify Needs and Activities to Support Stakeholders During Digital Transformation. >
Analyzing stakeholder interests and the impact of digital transformation efforts on them is critical to proper engagement planning... more »
About Wowledge
Wowledge is the expert-driven platform for lean teams building strategic HR programs. Members enjoy access to up-to-date best practices, step-by-step guides, tools, templates, and insights to accelerate the design and implementation of all key HR programs and processes.
Since each organization has unique characteristics, needs, and aspirations, Wowledge's practices are developed utilizing an exclusive stage-based approach—from Core to Advanced to Emerging—that reflects distinct levels of sophistication to meet our members where they are.
Build strategic HR programs with refreshingly easy-to-follow best practices.
Get started for FREE! Learn more.