The evolution of technology and the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) have left an indelible mark on how organizations approach Talent Strategy and staffing needs. In this digital age, the effective utilization of these applications is fundamental for HR professionals to navigate the complexities of the workforce. The "Six (6) Bs" of talent strategy, first identified by Dave Ulrich and updated by Adam Gibson, provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to manage their talent effectively. These Bs encompass “Buy, Build, Borrow, Bot, Bind, and Bounce,” each representing a critical facet of talent strategy.
Technology plays an instrumental role in facilitating the implementation of these strategies to achieve standardization, generate data-driven insights, and predict future talent requirements and gaps. Therefore, it is essential to understand the technologies that can be leveraged within each of the "6 Bs" to meet future staffing needs. These technological advancements not only streamline HR processes but also equip organizations with the tools to be more agile and responsive to the evolving demands of the modern workforce.
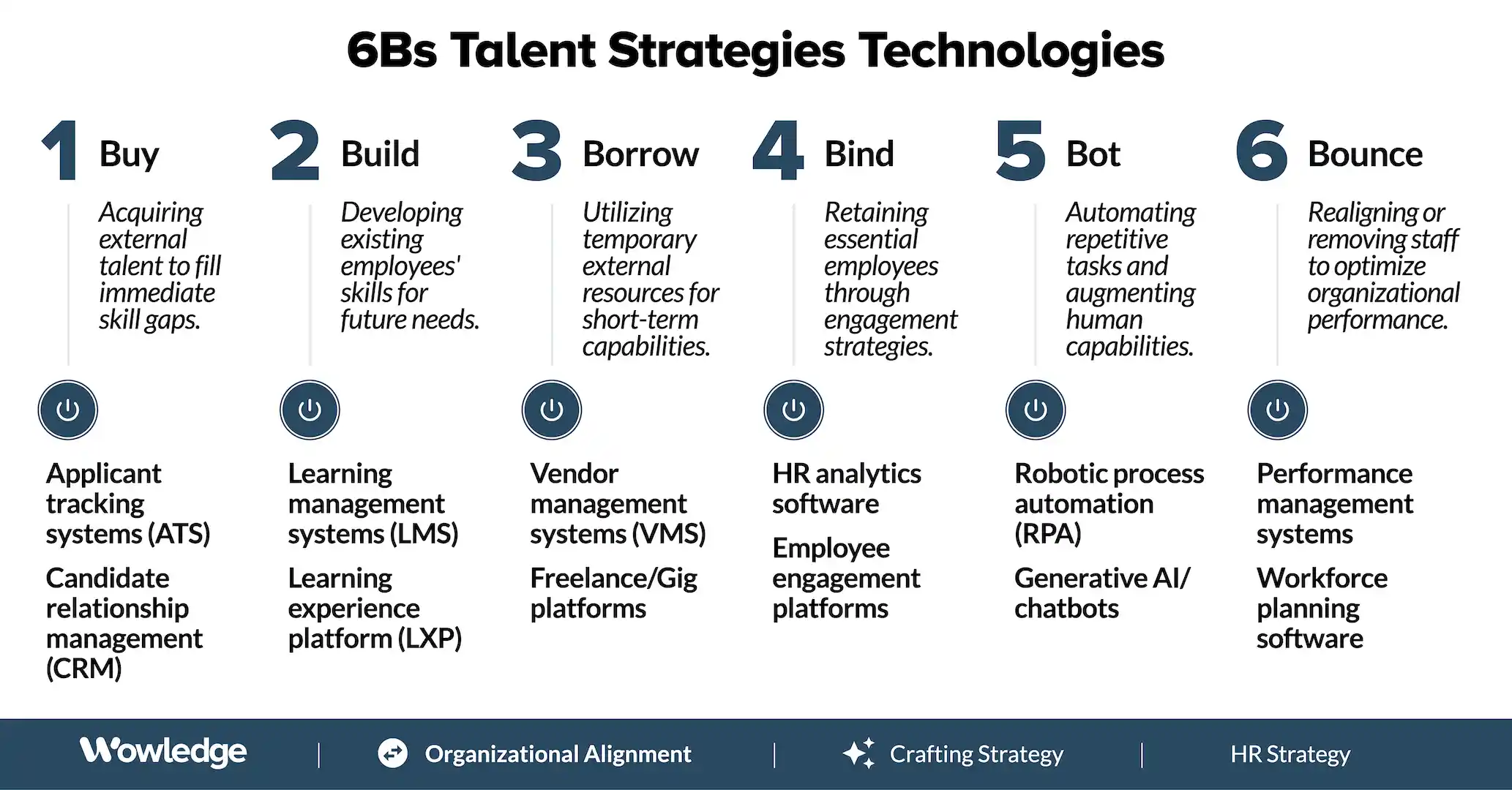
The 6 Bs Model:
- Buy - acquiring needed talent from external sources through active employee sourcing, attraction, and recruitment efforts.
- Build - developing the skills and abilities needed to fulfill business objectives from within the existing employee base through learning and development activities.
- Borrow - partnering with external organizations and individuals to use non-employee resources that fill skill needs on a project (e.g., contingent workers, contractors, or consultants) or time-limited (temporary or summer hire/intern) basis.
- Bind – creating tailored development, mobility, pay, or benefits programs to increase the engagement and retention of employees considered essential to the long-term success of the business.
- Bot - leveraging AI programming to automate repetitive tasks and reduce existing employees through conversational chatbots.
- Bounce – moving lower performing employees either out of the organization or into jobs better suited to their skills, abilities, and work styles.
These strategies are intended for use in an integrated fashion so that, together, all of the organization’s staffing and capability needs can be met simultaneously. The planning and coordination of these are critical elements typically driven by a combination of talent strategy and strategic workforce planning.
Talent Strategy Technologies to standardize processes, data collection, and reliability
Leveraging technology within the framework of the "6 Bs" of talent strategy to fulfill staffing needs can help standardize processes, data collection, and reliability.
Here's how technology can be applied to each of these areas:
1. Buy
- Standardized Processes: Use applicant tracking systems (ATS) and recruitment management software to standardize and streamline the recruitment process and workflows. AI-driven tools can help sort and shortlist candidates objectively, making the recruitment process more efficient. These ensure that each candidate goes through a consistent and well-documented process, from application to onboarding.
- Data Collection: ATS, candidate relationship management (CRM), and HR analytics tools can collect and store common data on candidate profiles, application sources, interview performance, current job status, and hiring outcomes. This data can be analyzed to refine the recruitment process and track candidates’ status and progress throughout the lifecycle.
- Reliability: Automation in the recruitment process reduces human error and bias, leading to more reliable and consistent hiring decisions.
2. Build
- Standardized Processes: Learning management systems (LMS) and learning experience platforms (LXP) enable organizations to standardize training content, delivery, and assessment. In addition, using skills-based and talent marketplace platforms provides transparency and shared access to open roles. Skills databases and employee self-assessment methods help identify current skills and future role requirements and gaps that need to be filled. These ensure that all employees receive consistent yet tailorable training and skill development opportunities.
- Data Collection: LMS, LXP, and HR systems can collect data on employee training progress and outcomes, while talent marketplaces collect skills data that can be leveraged to identify overlaps between career opportunities and existing skills. This data helps in tracking skill development and identifying areas where additional training is needed.
- Reliability: Technology-assisted training provides reliable content delivery, assessments, and tracking, ensuring employees receive consistent learning experiences and access.
3. Borrow
- Standardized Processes: Vendor management systems (VMS) standardize the procurement and management of contingent labor, with each contractor candidate and outsourcing company providing the same background, skills, availability, and cost data for comparisons. Freelance/Gig platforms also connect companies with freelance talent and contractors. These platforms make it easier to find and hire contingent workers quickly and efficiently and help ensure the contingent workforce meets the organization's needs and standards.
- Data Collection: VMS and contingent labor platforms collect data on worker qualifications, performance, and cost. This data helps organizations decide when and how to use contingent labor.
- Reliability: Standardized processes and data collection through VMS enhance reliability and transparency across contingent labor relationships that can be counted in the thousands.
4. Bind
- Standardized Processes: HR analytics and employee engagement platforms standardize the process of identifying retention risks and implementing tailored retention strategies. AI-powered predictive models can effectively project which employees are at risk of leaving.
- Data Collection: These tools collect data on employee engagement, satisfaction, and turnover trends, providing valuable insights for retention efforts.
- Reliability: Data-driven assessment and retention strategies are more objective, reliable, and effective in addressing critical staff retention challenges equally across employee segments, functions, and locations.
5. Bot
- Standardized Processes: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive and rule-based tasks. Chatbots and AI-driven systems standardize responses to common HR inquiries, ensuring that employees receive consistent and accurate information.
- Data Collection: Chatbots can collect data on employee inquiries and feedback, helping HR identify areas where improvements or additional support are needed.
- Reliability: AI chatbots provide reliable 24/7 support, reducing response time, providing consistent responses, and minimizing human errors in answering routine HR questions.
6. Bounce
- Standardized Processes: Performance management software standardizes the evaluation, feedback, and development planning processes for underperforming employees. Centralized systems track time, attendance, absenteeism, and leave use (and abuse) in a structured and consistent manner.
- Data Collection: These systems collect data on employee behavior, performance, improvement plans, and outcomes, enabling HR to make informed decisions about employment transitions.
- Reliability: Standardized processes and data collection enhance the fairness and reliability of performance management decisions.
How technology can be used to generate insights into talent needs, trends, and skills gaps
Technology plays a fundamental role in generating insights into talent needs, trends, and skills gaps across the different talent strategy options.
- Data Analytics: Applicant tracking systems (ATS), candidate relationship management (CRM), and HR analytics tools can analyze recruitment data to identify patterns and trends in the type and volume of candidates in high demand or short supply. These can also be leveraged to understand the typical job search patterns of candidates for different roles and job levels.
- Skills Gap Analysis: Technology can be used to assess the skills and qualifications of potential candidates within targeted talent pools and compare them to the skills required for current and future job roles, highlighting matches and gaps.
- Learning Analytics: Learning management systems (LMS, LXP) can track and analyze employee participation, progress, and performance in training programs. This data can identify areas where employees may need further development.
- Skills Assessment: Skills databases and supporting performance, learning, and career development-related technologies can be used to assess employee skills and competencies and compare them to evolving job requirements, pinpointing skills gaps that need to be addressed through training and development programs.
- Vendor Performance and Cost Metrics: Vendor management systems (VMS) can capture and analyze performance metrics of contingent labor providers. This information helps assess the quality and suitability of outsourced talent and providers. They can also track the costs associated with contingent labor and outsourcing, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions on whether to continue with these arrangements or explore alternative solutions.
- Employee Engagement Data: HR analytics and employee listening/engagement platforms can track employee sentiment, satisfaction, and engagement levels. This data can highlight trends in what keeps employees engaged and motivated and how those trends relate to retention, productivity, and performance. HR systems can also track certain life events, employee development, mobility, etc. for use in assessing their impact on retention challenges.
- Employee Queries and Feedback: AI chatbots can collect and analyze data on the most common HR-related employee inquiries and feedback. This information can be used to identify areas for HR process improvement and employee information needs. They can quantify the time, schedules, and resources used for routine HR inquiries, which can inform strategic resource allocation.
- Performance and Skill Analytics: Performance management and payroll/time and attendance systems can generate insights into employee performance and policy adherence, helping identify underperformers and areas that require improvement. Data on job-specific skills and competencies can be analyzed to determine whether an employee's skill set aligns with their current role or might be better suited for a different position.
How technology can be leveraged to predict future requirements
Technology can be harnessed within the "6 Bs" of talent strategy to predict future talent requirements and identify potential gaps. Here's how technology can help organizations anticipate future needs and proactively address talent gaps in each of these areas:
Buy: Applicant tracking systems (ATS) and HR analytics tools can analyze historical recruitment data, such as turnover rates, growth projections, and changing job roles, to forecast future hiring needs. Skills data can be updated to align with future business directions and then leveraged to assess current staffing to identify future gaps in requirements. By continuously assessing the skills of incoming candidates and comparing them to evolving job requirements, technology can project potential skill gaps and shortages.
Build: Technology can be used to create and maintain skill requirements and competency models for various roles. Regular skills assessments help identify gaps between employee skill sets and future job requirements. Learning management systems (LMS, LXP) and talent marketplace technologies can produce data for predictive analytics to anticipate future training and development needs based on employee career paths and business goals.
Borrow: Technology can monitor market and industry trend data to predict when contingent labor is in higher demand and the availability of specific skills in the market. Organizations can use technology to model and predict the cost-effectiveness of using contingent labor or outsourcing based on historical data and future projections.
Bind: HR analytics tools can predict retention risks by analyzing historical data and leveraging that in regression and related predictive analytics. In that way, organizations can develop models that assess employee flight risks and help determine where to focus retention efforts.
Bot: AI chatbots can track and analyze the types of HR inquiries and issues they handle. By identifying patterns and trends, organizations can anticipate where chatbots can be further deployed to address future inquiries.
Bounce: Technology can be used to analyze performance metrics and historical performance data to predict which employees are at risk of underperforming or identify where skills misalignments exist. By assessing employee skills and competencies, organizations can predict if employees' skill sets will likely match their current or future job roles. Payroll systems can produce reporting highlighting excessive tardiness, absenteeism, sick leave abuse, and other non-compliance with work hours and attendance policies.

Enabling Practices & Resources
HR Technology has advanced to a level where it is currently capable of offering scalable productivity gains in processing HR transactions, with emerging technologies capable of recognizing trends and recommending solutions to those issues.
Applicant tracking systems (ATS) help streamline and manage all phases of the recruiting process from candidate sourcing to hiring. They offer many advantages to the organization not only in terms of gained efficiencies but are also a relevant component of the candidate experience.
Current technologies offer the promise of tremendous efficiencies in the development and handling of career development processes and insights.
